![]() Go to frame view (Recommended only for
screen resolution 1024x768)
Go to frame view (Recommended only for
screen resolution 1024x768)
3.2 Nomenclature and Isomerism
Depending on the positions occupied by the phosphate group in ribo- or deoxyribonucleoside, distinction is made between three types of (isomeric) nucleotides:
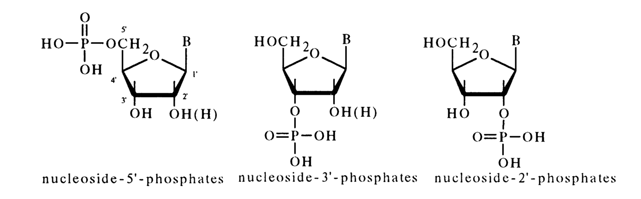
A nucleotide's name is usually based on that of the associated nucleoside. In the most common version, it consists of the nucleoside's name and position of the phosphate. For example, uridine 5'-phosphate:
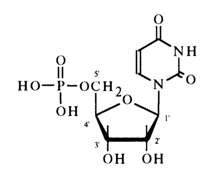
An alternative name of this nucleotide is 5-uridylic acid. In the case of
pyrimidine nucleotides, the nomenclature consists of the name of the corresponding
nucleoside (uridyl, cytidyl, etc.) plus the ending "ic" and the word
"acid". For example: uridyl + ic acid = uridylic acid. Purine nucleotides have
similar nomenclature with the difference that the basic component is the name of the
corresponding base (guanyl, adenyl, etc.). For example: guanyl + ic acid = guanylic acid.
The composite name is always preceded by the position of the phosphate in the nucleotide ![]() . Adenosine 3'-phosphate, for instance, may
also be called 3'-adenylic acid.
. Adenosine 3'-phosphate, for instance, may
also be called 3'-adenylic acid.
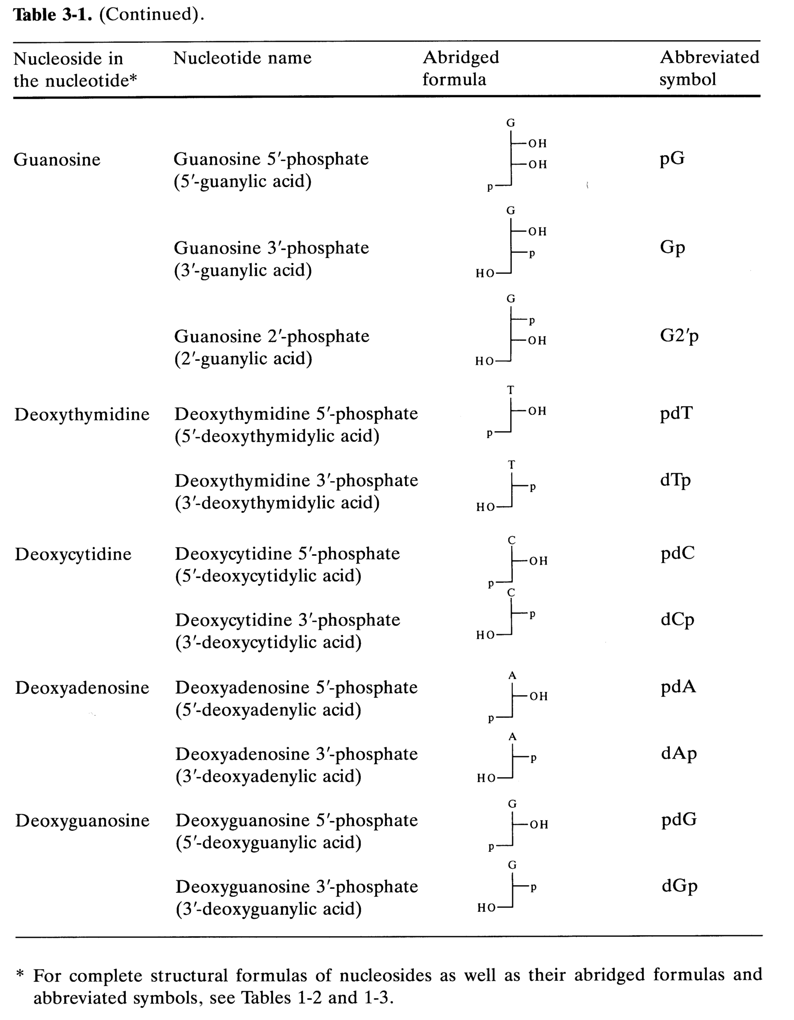
Table 3-1 lists the names of the major nucleotides isolated from natural nucleic acids (DNA and RNA). Also listed are abridged formulas and abbreviated symbols, which, in turn, are based on abridged formulas and abbreviated symbols for the corresponding nucleosides plus an abbreviated symbol of the phosphate group. According to the rules of IUPAC and IUB, the phosphate is designated as "p". The abridged formulas for the above nucleotides are as follows:
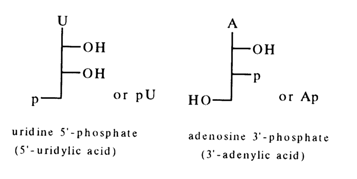
It can be seen that even more abbreviated symbols consisting of only two letters are used for nucleotides, the capital letter corresponding to the name of the nucleoside (see Table 3-1) and the small letter (p) on the left indicating that there is a phosphate group at position 5'. If the phosphate group is linked to the carbohydrate moiety at position 3', the letter "p" is placed to the right of the capital letter (symbolyzing the nucleoside). The presence of a phosphate group at position 2', in guanosine 2'-phosphate, for example, is indicated as follows:
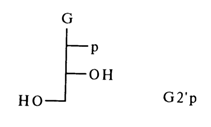
In the case of deoxynucleotides, the letter "d" is added before the symbol.
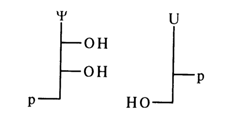
The names and abbreviated symbols of nucleotides that are derivatives of minor nucleosides (see Tables 1-5 and 1-6) are based on the same principle. For instance, pseudouridine 5'-phosphate (5'-pseudouridylic acid) has the abbreviated symbol p
Y, while deoxyuridine 3'-phosphate (3'-deoxyuridylic acid) has the symbol dUp.Their abridged formulas are as follows: